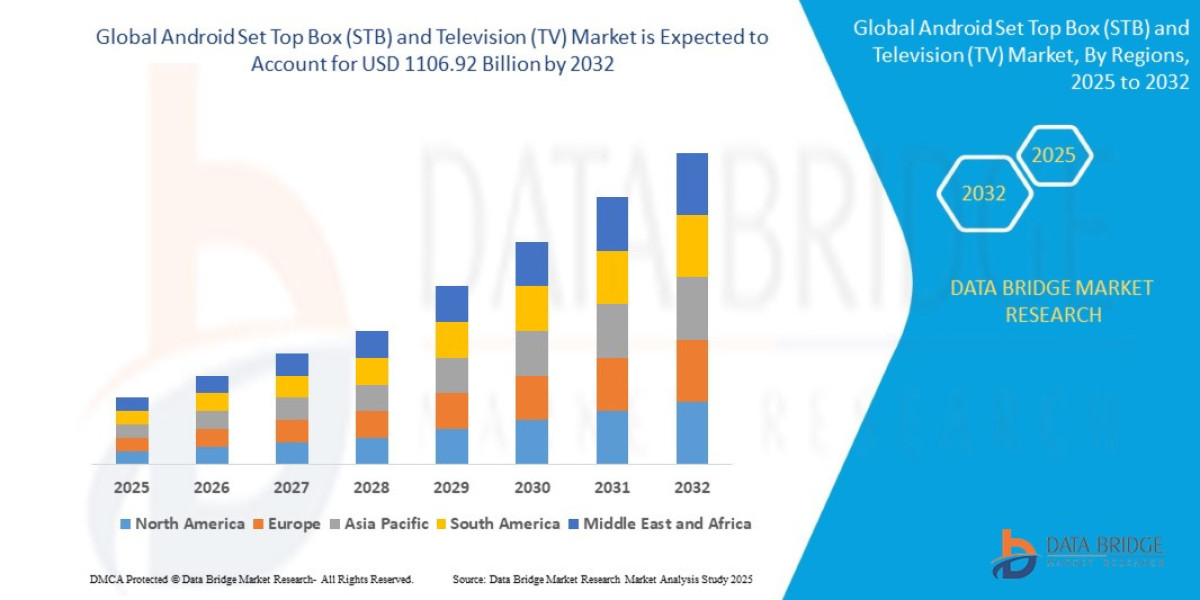
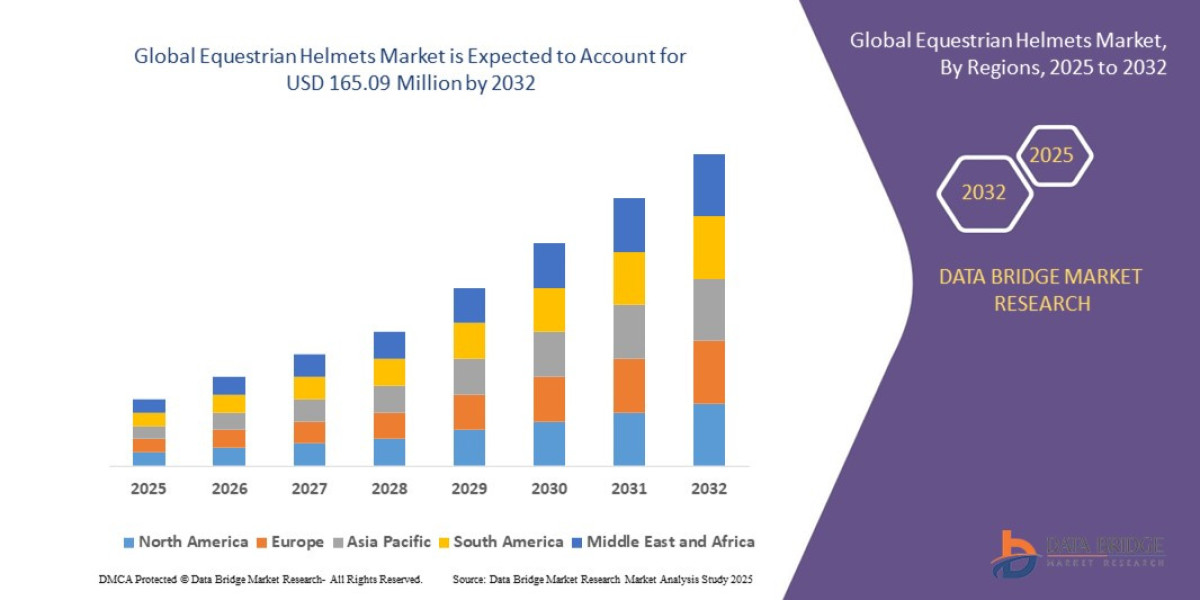
Ancillary Services Power Industry – Covers companies providing grid support services, including frequency regulation, reserve power, and voltage management.
The Ancillary Services Power Industry encompasses the entire ecosystem of organizations, technology providers, regulators, and service implementers that facilitate the provision and consumption of grid support services. It is a critical, though often less visible, segment of the broader electric power sector, focused entirely on system security and quality of supply. The industry's function is to develop the capabilities—both physical assets and control mechanisms—that TSOs and DSOs rely on. The industry's value proposition is centered on reliability and flexibility.
The ecosystem features a complex value chain involving several key actors. At the core are the grid operators (TSOs and DSOs), who specify the technical requirements for each service, setting the standards for response time, duration, and accuracy. Supporting these operators are technology and equipment manufacturers, who supply everything from high-speed battery inverters and flexible gas turbines to advanced software for system monitoring (SCADA) and predictive analytics (AI/Machine Learning). These technological advancements are essential for integrating new, non-traditional service providers.
Shutterstock
Service providers form another crucial component. This includes large Independent Power Producers (IPPs), who retrofit their existing generators to offer reserve capacity, and new entrants like energy storage developers and demand response aggregators. The latter act as intermediaries, coordinating the load reduction or power injection from hundreds or thousands of distributed resources (such as commercial HVAC systems, electric vehicle chargers, or rooftop solar). The regulatory and policy bodies also play a pivotal, non-monetary role, as they establish the market rules, define the services, and determine the technical standards for participation, which fundamentally shapes the industry's evolution. The transition to a power system dominated by variable renewable energy (VRE) has forced the industry to innovate rapidly, shifting away from a reliance on the inherent stability (inertia) of large synchronous generators toward fast-acting, synthetic flexibility provided by inverter-based resources (IBR) like batteries and solar farms. This qualitative shift defines the modern trajectory of the Ancillary Services Power Industry.
FAQs on Ancillary Services Power Industry
Q: What is the role of a Demand Response Aggregator in this industry?
A: An aggregator acts as a middleman, collecting small amounts of load reduction or generation capacity from many distributed consumers and packaging them into a sufficient quantity to participate in the bulk ancillary services market.
Q: How has the rise of renewable energy sources impacted this industry?
A: It has increased the demand for fast-acting ancillary services, as VRE sources are intermittent and lack the natural inertia of traditional plants. This drives the need for new technologies like battery storage and smart inverters.
Q: What technology is crucial for the modern operation of this industry?
A: Smart grid technologies and high-speed communication infrastructure are crucial for real-time monitoring and control, enabling the TSO to dispatch services from geographically dispersed and diverse providers (DERs) in milliseconds.
More Related Reports: